Modern piping and ducting systems are constantly exposed to temperature, pressure, vibration, and other operating loads, making it impossible for them to remain in one form.
As a result, these systems are continually expanding, contracting, and shifting. If not properly managed, such movement can lead to excessive stress on pipes, leakage, misalignment and premature system failure. Utilising expansion joints is critical for this reason.
Expansion joints are components that make it possible for piping systems to flex and absorb vibration. When the duct or pipeline's temperature rises, the fluid in the duct or pipeline also rises.
To control these increasing temperatures an expansion joint provides a flexible portion in a piping system that moves with the rising temperature. This increase in temperature causes the duct/pipeline to expand as well. On the downside, as the temperature of the fluid decreases the duct/pipeline will also decrease in size consequently. Expansion joints will relieve this issue by providing "flexibility" to the duct/pipeline thus allowing them to "flex" and "adjust" to the duct/pipeline's operating conditions and protect the various equipment connected to it.
“A wide variety of industries such as power generation, oil and gas, marine, HVAC, chemical processing, and manufacturing require the utilization of expansion joints to ensure safe, efficient and reliable operation of the system over a long period of time.”
This blog will describe in greater detail about Expansion Joints. The following topics will be covered in this blog: Different types of Expansion Joints; Types of materials used in the manufacturing of Expansion Joints; Design features of Expansion Joints; Advantages of using Expansion Joints; Applications of Expansion Joints; How are Expansion Joints designed to accommodate for growth/shrinkage and lateral movement; And how to select Expansion Joints.
Flexible mechanical components used to compensate for the movement caused by thermal expansion, mechanical vibration/pressure variation, and structural settling; expansion joints can be found in ductwork and exhaust systems, as well as piping. Without them, rigid pipe systems would experience excessive amounts of stress, resulting in cracks, leaks, and damaged equipment.
The purpose of expansion joints is not only to provide movement compensation but they also help to decrease vibration, noise, and mechanical load to motors and turbine engines, blower motors, and other connected machinery. They can be utilized in both small systems and large-scale industrial networks, where operational stability is paramount to success.
It's also important to note that companies such as Flexibel design and manufacture custom designed expansion joints that meet the demanding application of extremely high-pressure/high temperature/vibration-based operations, providing constant reliability under these conditions.
There are several types of expansion joints, each designed to suit specific operating conditions, movement requirements, and media compatibility.
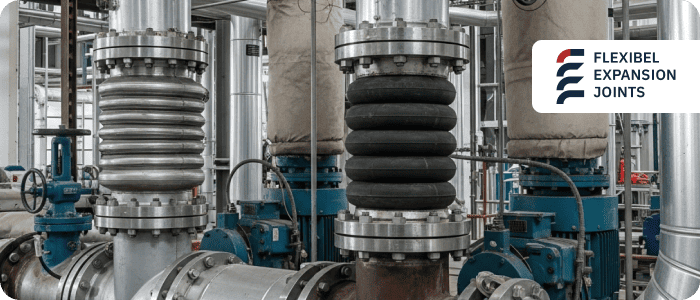
Metallic Expansion Joints, Metallic Joints or Metal Expansion Joints consist of metallic thin-wall bellows usually constructed of, but not limited to, Stainless Steel and/or high-quality alloys. They facilitate axial, lateral, and angular movements with the necessary support for the structures surrounding them when installed.
The Metallic Expansion Joint exhausts gas from the turbine in a Power Plant; feed water from the Boiler to the Turbine in a Refinery; feed gas to a Gas Turbine in a Petrochemical Facility; steam throughout a Steam Network; and marine industrial applications where Structural Integrity and Performance are of utmost importance.
Rubber Expansion Joints are flexible connectors created from a material category known as elastomers, elastomeric (also known as rubber) are made from a family of materials such as EPDM, neoprene and nitrile. The various types of flexible connectors include rubber expansion bellows, rubber flexible joint and rubber bellow joint designs.
The Rubber Expansion Joint is mainly used for isolating vibrations, absorbing small amounts of motion or for reducing noise. Rubber expansion joints are frequently utilised in HVAC systems, water treatment facilities, pump or motor connections, and general industrial piping applications. Rubber expansion joints manufacturers specifically design to increase their ability to withstand pressure.
Fabric Expansion Joints are a type of flexible solution that can be used in many different applications where high temperatures and low pressures exist. Fabric joints can commonly be found in duct systems, exhaust lines, flue gas systems, and air handling units.
A Fabric Expansion Joints Manufacturer creates types by layering multiple types of fabric together as well as using various types of insulation and coating materials to accommodate the thermal movement of the fabric due to thermal expansion/contraction, vibration, and exposure to corrosive gases. In addition, Fabric Expansion Joints are an excellent option in situations where metal joints cannot be used because of the weight limitations and/or concern with the corrosive nature of the gas being handled.
Metallic hoses are another term for Metal Hose or Metallic Hose, which are flexible metal assemblies designed to allow absorption of vibration and movement, while still maintaining flow integrity. Hoses are typically utilized in conjunction with expansion joints in applications that require flexibility and durability.
Metallic hoses are frequently found in applications that are subject to high-pressure conditions, high temperatures and/or vibrations such as engine connections, fuel lines and industrial piping systems.
Read More: Quality Manufacturer Of Bellow Expansion Joint For Modern Industries
Expansion joints provide a major benefit in that they take on the movement produced by the piping system and relieve it from all of the components of the piping system. This absorption of movement from thermal expansion and contraction prevents leaking from the piping systems and prevents damage to the piping systems.
The expansion joints also suppress vibration and noise within the piping systems and increase the efficiency of their operation, protect sensitive equipment, and increase the durability of the piping system.
The combination of the above characteristics allows for the extended service life of piping systems, lower maintenance costs, and increased operational safety.
Expansion joints have a variety of applications in many different industries.
Also See: Expansion Joints: Custom Solutions For Industrial Applications
Expansion joints have several parts that work together to control the following aspects: Movement (relative to the pipe), Pressure, and the Environment (flow through them).
While the type of movement/bellows has been discussed previously in terms of the different styles (accordion type vs. ring-type), the remaining components are determined by how the expansion joint will function for each application (e.g., installation site, pressure rating, temperature, etc.). As long as each of these components has been designed according to these requirements, your custom expansion joint will operate within safe limits and last for many years without any problems.
The type of material used to manufacture all of the different types of expansion joints will depend on what is required for a particular application. For the case of metallic expansion joints and metallic hoses, metals like stainless steel and various speciality alloys are used; for rubber expansion joints, internal elastomers are used; for fabric expansion joints, coated fabrics and insulation materials are used.
The selection of the right material will enable the manufactured joints to be chemically compatible, able to withstand the temperature range required for the application, and durable enough for the application.
Expansion joints are designed to flex in the axial direction, lateral direction, custom direction (angular) or a combination of these movements. The capability of these joints to accommodate movement is dependent on the type, design and the materials used to manufacture the joint.
Most metal joints are constructed to withstand complex movements along with extremely high stress, whereas rubber joints and fabric joints provide the greatest flexibility with respect to compensating for vibration and misalignment.
There are many reasons expansion joints fail, and the most frequent ones are due to selection errors, installation mistakes, excessive movement beyond the design limits (i.e., expansion / contraction), rust, and neglectful upkeep. A frequent example is using a different kind of expansion joint than is rated for your application in the door closing area, which can mean considerably shortening the life expectancy of that piece of equipment.
Nevertheless, by routinely inspecting and/or periodically examining an expansion joint, and ensuring you have designed your system properly, you will most likely mitigate the chance of experiencing pre-mature failures in that expansion joint.
Choosing the correct type of expansion joint for your application requires an understanding of the operating conditions (i.e., pressure, temperature, movement and media). Most systems with high pressure and high temperature will use metal expansion joints. Systems that generate significant vibration will normally use rubber expansion joints or fabric expansion joints.
Other factors to consider when selecting an expansion joint include installation space, maintenance access and industry standards. Partnering with an experienced manufacturer such as
Piping and ducting systems can benefit from the use of expansion joints because they protect the systems from stress, vibration, and thermal movement. The use of metallic expansion joints, rubber expansion joints, and fabric expansion joints, as well as metallic hoses, can help increase the reliability, safety, and efficiency of systems.
By learning about the various types and materials that are available for use, industries can design systems that will operate consistently and withstand adverse environmental conditions.